
Syed Shayan Real Estate Archive

From Real Estate History
On 26 November 1947 the Government of West Punjab completed its first major survey of Evacuee Property, documenting thousands of abandoned agricultural lands urban buildings and industrial units left behind during the mass migration of Partition. The survey established the first verified list of transferable assets that could be allocated to incoming Muslim refugees from East Punjab and northern India.
Municipal teams recorded street widths drainage paths property boundaries and ownership claims across almost fifteen thousand villages and towns. These verified lists became the basis for temporary and later permanent allotments to displaced families. The effort formed a critical administrative link between the chaos of migration and the creation of a new urban and rural ownership structure in Pakistan.
▪ Reference(s):
تقسیم ہند کے بعد لاکھوں افراد کی ہجرت کے نتیجے میں چھوڑی گئی جائیدادوں کے انتظام کا سنگین بحران پیدا ہوا تھا۔ مغربی پنجاب میں اس مسئلے سے نمٹنے کے لیے 26 نومبر 1947 کو ایوکیوئی پراپرٹی کے پہلے بڑے سروے کی بنیاد پر قابلِ انتقال املاک کی فائنل لسٹ جاری کی گئی، جس نے مہاجرین کی آبادکاری اور شہری و دیہی زمینوں کی نئی ملکیت کے ڈھانچے کو متعین کیا۔
ابتدائی اقدامات کے تحت 29 اگست 1947 کو “کیسٹوڈین آف ریفیوجیز پراپرٹی” کا نظام قائم کیا گیا تھا، جس کے بعد 23 ستمبر 1947 کو ویسٹ پنجاب حکومت نے Administration of Evacuee Property Act نافذ کیا۔ اس قانون کا مقصد ایوکیوئی جائیدادوں کی حفاظت، ان کی فہرست سازی اور فوری الاٹمنٹ کے انتظامات تھے۔
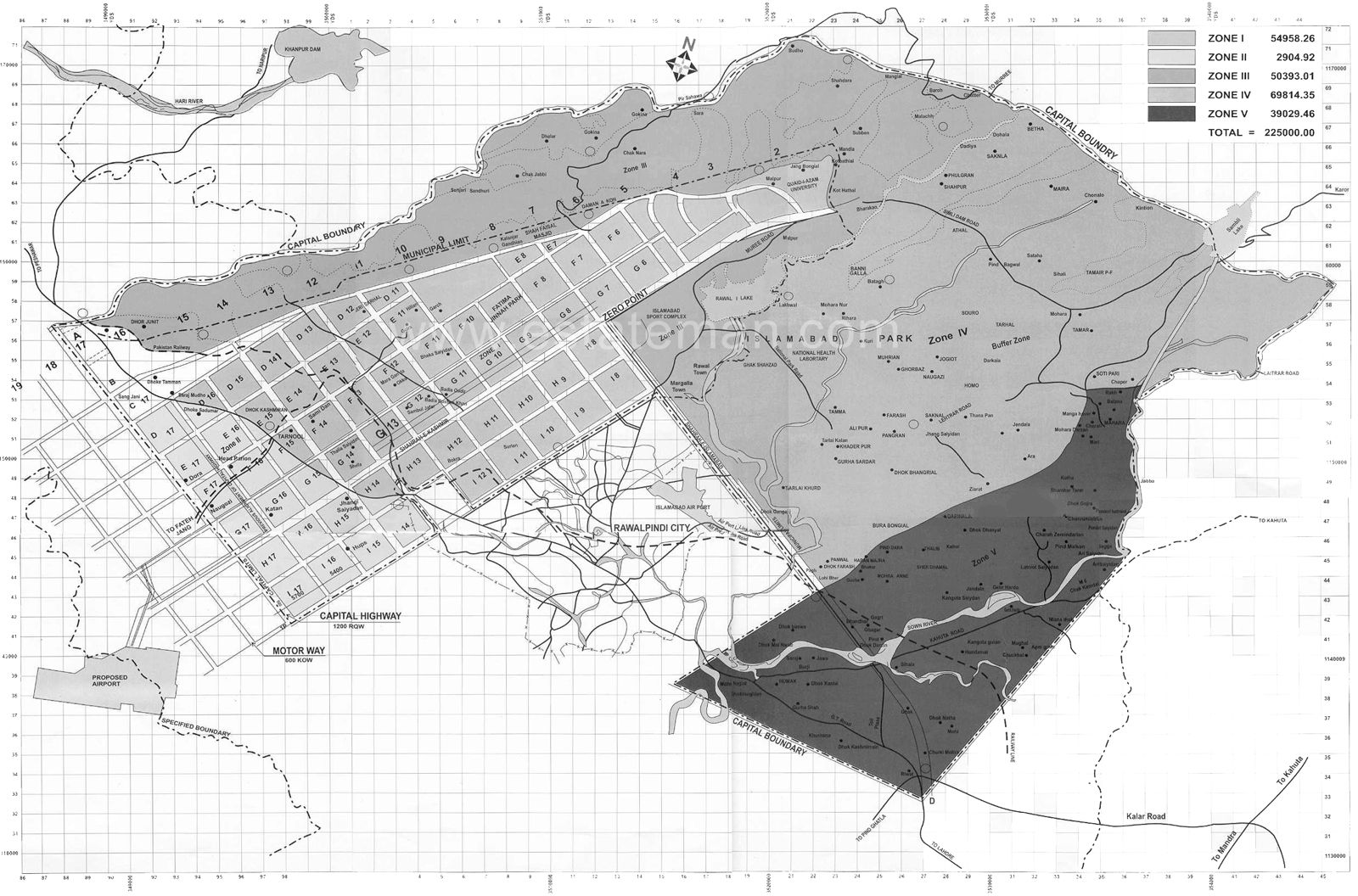
On this date, the Capital Development Authority formally approved the first sector boundary map for Pakistan’s newly designated federal capital, Islamabad. The authorisation marked one of the earliest and most consequential administrative steps taken by the newly formed authority, which had been established in June 1960 under the direction of President Muhammad Ayub Khan.
Prepared within the framework of the master plan developed by Doxiadis Associates of Athens, the boundary map confirmed the geometric layout of the F, G, H and I series sectors, forming the structural grid that would shape the capital’s long-term growth. The CDA chairman at the time, Major General Yahya Khan, described the approval as the foundational “planning DNA” of the new city.
Structure and Intent of the Sector Plan
Under the Doxiadis plan, Islamabad was conceived as a modern, orderly and environmentally integrated capital. The adopted boundary system arranged the city on a two by two kilometre grid, with each sector divided into four sub-sectors planned as self-contained communities. Residential, commercial, educational and recreational functions were placed within walkable distances, framed by green belts intended to protect natural landscapes.
F Series: Predominantly residential in nature, the F sectors were designed to house middle and lower-middle income groups, including federal employees. Early development was prioritised in F-6 and F-7, with planned parks, pedestrian routes and green buffers.
G Series: The G sectors were positioned as central residential and community zones. G-6, the first to be developed, was designed to be completed by the end of 1960, with markets, schools, mosques and health facilities integrated into its layout.
I Series: The I sectors served the industrial and commercial functions of the new city. Areas from I-8 to I-17 were assigned for light industry, transport hubs and office clusters, forming the economic base of Islamabad.
H Series: Reserved for higher-income residences and institutional development, the H sectors were planned to accommodate universities, hospitals and cultural facilities, establishing Islamabad as an administrative and academic centre.
Planning Philosophy and Long Term Significance
The approval reflected the Doxiadis concept of a “Dynapolis”, a city designed to expand gradually from the north-east to the south-west, preserving existing villages while creating space for controlled urban growth. Road hierarchies were calibrated at 100-foot dual carriageways, 80-foot single lanes and dedicated pedestrian pathways, ensuring orderly circulation and low environmental impact.
President Ayub Khan, while reviewing the approved boundaries, remarked that Islamabad was intended not only as the administrative heart of Pakistan but also as “a model Asian city”, combining human needs, natural setting and modern technology.
The 26 November approval laid the administrative and spatial foundations for all future development. It enabled the CDA to begin land acquisition, allocate resources and initiate phased construction. Work on F-6 and G-6 was scheduled for commencement in early 1961, with core infrastructure projected for completion by 1963.
Historical Context
The decision to relocate the capital from Karachi to a new site near Rawalpindi was taken in 1959 following a national review of administrative needs, geography and security. Doxiadis Associates submitted the first draft of the master plan in May 1960, and the boundary approval of November 1960 represented the earliest formal adoption of that plan.
Legacy
This boundary authorisation became the cornerstone of Islamabad’s urban identity. The grid it introduced remains intact to this day, guiding municipal planning, land regulation and infrastructure development. It is widely regarded as one of the most influential planning decisions in Pakistan’s urban history.
▪ Reference(s):

کیپیٹل ڈویلپمنٹ اتھارٹی نے آج پاکستان کے نئے منصوبہ بند دارالحکومت اسلام آباد کے پہلے سرکاری سیکٹر باؤنڈری میپ کی باضابطہ منظوری دے دی ہے۔ یہ منظوری ایف (F)، جی (G)، آئی (I) اور ایچ (H) سیریز کے سیکٹروں کے لیے دی گئی ہے، جو شہر کے ماسٹر پلان کی بنیادی اکائیوں میں شمار ہوں گے۔ سی ڈی اے کے چیئرمین میجر جنرل یحییٰ خان نے اس منظوری کو “شہر کی مستقبل کی ترقی کا بنیادی نقشہ” قرار دیا ہے۔
یہ فیصلہ سی ڈی اے کی تشکیل کے چند ماہ بعد سامنے آیا ہے۔ اتھارٹی جون 1960 میں صدر ایوب خان کے حکم پر قائم کی گئی تھی، جسے اسلام آباد کی تعمیر، اراضی کے حصول، ترقیاتی کاموں اور ضابطوں کی نگرانی کی ذمہ داری دی گئی۔ یونانی ماہر شہر ساز کمپنی ڈوکسیاڈیس ایسوسی ایٹس کی تیار کردہ ماسٹر پلان کے مطابق شہر کو گرڈ آئرن نظام میں تقسیم کیا گیا ہے، جہاں ہر سیکٹر تقریباً دو کلومیٹر ضرب دو کلومیٹر کے مربع پر مشتمل ہوگا اور چار سب سیکٹروں میں تقسیم ہوگا۔
سیکٹروں کی تفصیلات اور منصوبہ ▫بندی
ایف سیریز (F Series)▫
یہ سیکٹرز بنیادی طور پر رہائشی علاقوں کے لیے مختص ہیں۔ ایف 6 اور ایف 7 جیسے سیکٹرز میں سرکاری ملازمین کی رہائش کے ابتدائی انتظامات کیے جائیں گے۔ گرین بیلٹس، پارکس، پیدل راستے اور مقامی سہولیات ہر سیکٹر کا لازمی حصہ ہوں گے۔
جی سیریز (G Series)▫
جی 6 کو اسلام آباد کا پہلا مکمل رہائشی سیکٹر قرار دیا گیا ہے، جو 1960 کے آخر تک تیار ہونے کی امید ہے۔ یہاں مارکیٹس، سکولوں، مساجد اور ہسپتالوں کی تعمیر ماسٹر پلان کے مطابق کی جا رہی ہے۔ جی سیریز شہر کے مرکزی حصے میں واقع ہے اور انتظامی دفاتر سے قریب ہے۔
آئی سیریز (I Series)▫
یہ سیکٹرز صنعتی، کمرشل اور ٹرانسپورٹ سرگرمیوں کے لیے مخصوص کیے گئے ہیں۔ آئی 8 سے آئی 17 تک کے علاقوں میں چھوٹی صنعتیں، کاروباری دفاتر، اور ٹرانسپورٹ ہبس قائم کیے جائیں گے۔ یہ اسلام آباد کی اقتصادی سرگرمیوں کا مرکز ہوں گے۔
ایچ سیریز (H Series)▫
ایچ 8 سے ایچ 17 تک کے سیکٹرز اعلیٰ تعلیم، ہسپتالوں اور جدید رہائش کے لیے مختص ہیں۔ یہاں یونیورسٹیاں، تحقیقاتی ادارے اور تفریحی مراکز شامل ہوں گے۔ سی ڈی اے کے مطابق ایچ سیریز اسلام آباد کو ایک علمی و صحت کے مرکز میں تبدیل کرے گی۔
شہر کی منصوبہ بندی کا ڈھانچہ▫
سی ڈی اے کے مطابق باؤنڈری میپ کی منظوری سے شہر کی یکساں اور سائنسی بنیادوں پر ترقی ممکن ہو سکے گی۔ ماسٹر پلان میں “ڈائناپولیس” (Dynapolis) کا تصور شامل ہے، جس کے تحت شہر شمال مشرق سے جنوب مغرب تک منظم توسیع کے قابل ہوگا۔ ہر سیکٹر کے گرد گرین بیلٹس آلودگی اور شور سے تحفظ فراہم کریں گی۔
شہر کے روڈ نیٹ ورک کو درج ذیل درجہ بندی کے مطابق ترتیب دیا گیا ہے:
– سو فٹ چوڑی ڈبل روڈز
– اسی فٹ چوڑی سنگل روڈز
– پیدل سفر کے لیے علیحدہ راستے
تاریخی پس منظر اور اہمیت▫
1959 میں کراچی کے بجائے نیا دارالحکومت تعمیر کرنے کا فیصلہ کیا گیا۔ راولپنڈی کے قریب موجود خطہ ماہرین کے مطابق موسمی، جغرافیائی اور دفاعی طور پر موزوں تھا۔ ڈوکسیاڈیس ایسوسی ایٹس نے مئی 1960 میں ابتدائی ماسٹر پلان پیش کیا، جس کے فوراً بعد سی ڈی اے قائم کی گئی۔
صدر ایوب خان کے مطابق “اسلام آباد نہ صرف پاکستان بلکہ خطے کا ایک ماڈل شہر ہوگا، جہاں جدید ترقی، قدرتی ماحول اور شہری ضرورتوں کا توازن قائم ہوگا۔”
ماہرین کا کہنا ہے کہ سیکٹر باؤنڈری میپ کی منظوری اسلام آباد کی طویل المدتی شہری شناخت کا پہلا بنیادی قدم ہے۔
چیلنجز اور مستقبل کے منصوبے▫
سی ڈی اے کے مطابق تعمیرات کے آغاز میں اراضی کے حصول، فنڈنگ اور مشینری کی فراہمی کے چیلنجز موجود ہیں، لیکن حکومتی حمایت کے بعد منصوبہ تیزی سے مکمل ہوگا۔ پہلے مرحلے میں ایف 6 اور جی 6 پر ترقیاتی کام شروع کیے جائیں گے اور 1963 تک بنیادی تعمیر مکمل کرنے کا ہدف رکھا گیا ہے۔
شہریوں سے اپیل کی گئی ہے کہ وہ منصوبہ بندی کے اصولوں کے مطابق تعاون کریں تاکہ اسلام آباد کو دنیا کے بہترین دارالحکومتوں میں شامل کیا جا سکے۔
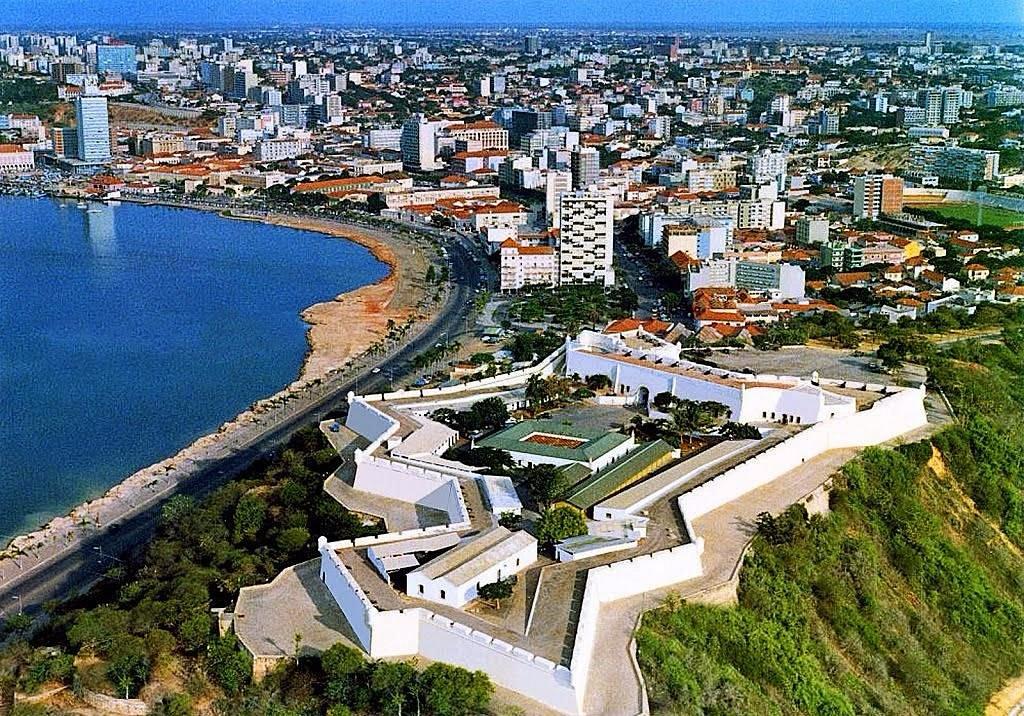

25 January 1575 marks the formal foundation of Luanda on the western coast of Africa by the Portuguese explorer and colonial administrator Paulo Dias de Novais. The settlement was originally named São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda, a designation that was later shortened to Luanda. At the time of its establishment in 1575, Luanda was a small col...
Read More →
On October 26, 2018, blockchain technology began transforming real estate transactions through pilot programs testing property tokenization and smart contracts. This innovation promised to revolutionize property ownership transfers, title management, and transaction recording by creating immutable, transparent digital ledgers. Early adopters explor...
Read More →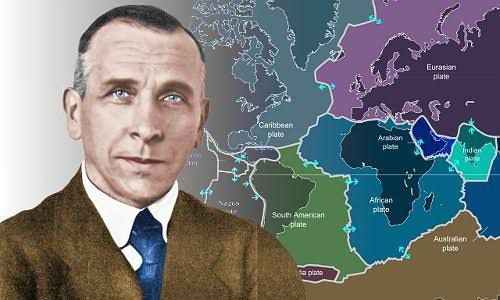
On 6 January 1912, the German geophysicist and meteorologist Alfred Wegener presented for the first time the theory of continental drift during a meeting of the German Geological Association held at the Senckenberg Museum in Frankfurt. In this lecture, Wegener proposed that the Earth’s continents had not always occupied their present positions bu...
Read More →
On this day in 2005, a catastrophic 7.6 magnitude earthquake struck northern Pakistan and Azad Jammu & Kashmir (AJK), marking one of the deadliest natural disasters in the nation’s history. Within minutes, vast regions of Muzaffarabad, Balakot, and Bagh were reduced to rubble. Over 73,000 people lost their lives, while millions were left injured ...
Read More →
On 2 February 1665, British forces formally consolidated their control over the Dutch colonial settlement of New Amsterdam, located in what is now the Manhattan area of New York City. On this occasion, the settlement was renamed New York. The earliest known name of the area was Manahatta or Mannahatta, a term used by the indigenous Lenape people, ...
Read More →
The acquisition of land for the Model Town Society was one of the most remarkable and spirited chapters in its early history. Dewan Khem Chand and his...

Between 1921 and 1924, the land for Model Town Lahore was acquired in successive phases. The process began in 1921, shortly after the establishment of...
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!