
Syed Shayan Real Estate Archive

From Real Estate History
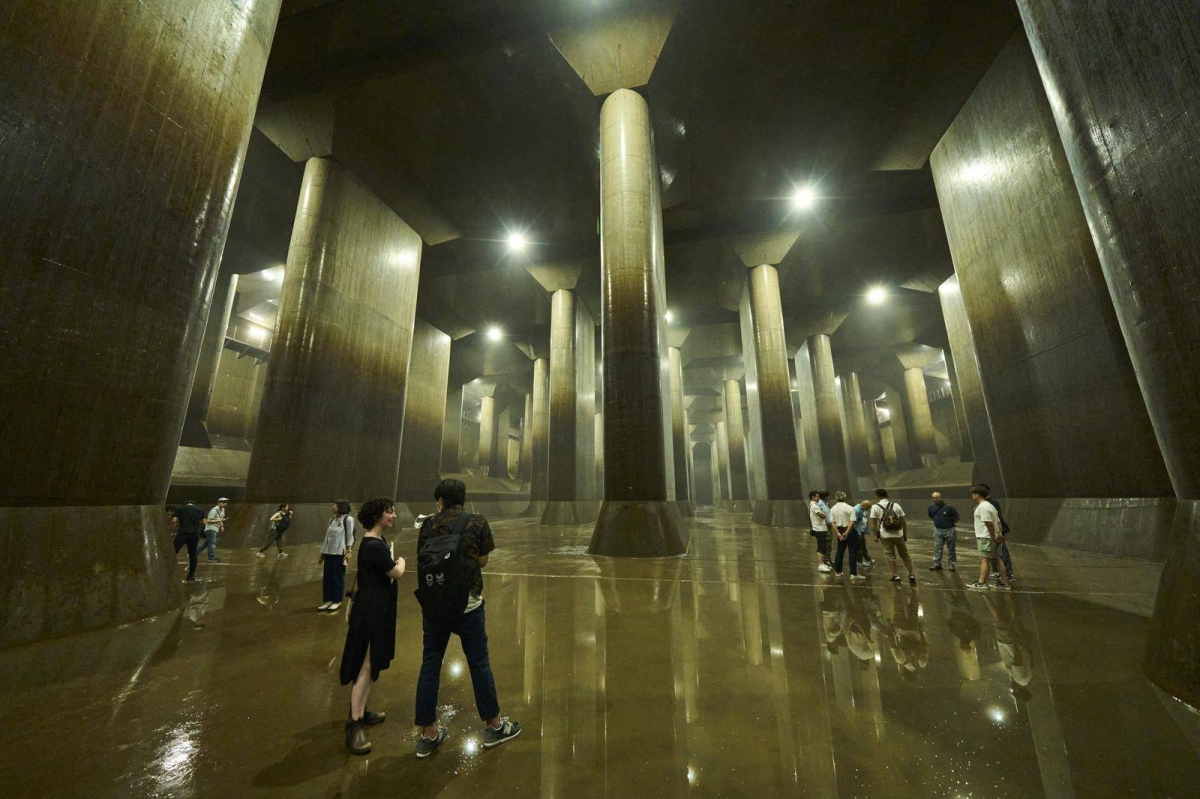

On November 21, 1979, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government released one of Japan’s earliest comprehensive flood-resilient urban infrastructure blueprints, responding to a decade of frequent typhoons and rising urban density. During the 1970s, Tokyo had experienced repeated flood emergencies due to overwhelmed drainage channels and rapid concrete expansion that reduced natural water absorption. The new blueprint proposed an interconnected system of underground flood reservoirs, widened river embankments, multi-level drainage tunnels, and protected greenwater retention parks distributed across high-risk wards. It emphasized long-term land-use planning and mandated that new industrial and residential projects incorporate permeable surfaces, rooftop rainwater capture structures, and overflow mitigation mechanisms.
The blueprint also marked Japan’s early shift toward scientifically modelled hazard forecasting. Engineers used rainfall simulations and terrain-based computational mapping to predict high-risk zones, allowing Tokyo to integrate flood protection into zoning regulations for the first time. Socially, the plan played a major role in improving public awareness regarding flood preparedness and building safety, with local committees conducting workshops to encourage household-level resilience practices.
Over time, this 1979 framework became the philosophical and technical foundation for Japan’s later mega-projects, including the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel and multi-tiered stormwater tunnels built in the 1990s. Tokyo’s transformation into one of the world’s most flood-resilient megacities began with this blueprint, which continues to influence contemporary Japanese urban infrastructure strategy.
▪ Reference(s):

21 نومبر 1979 کو ٹوکیو میٹروپولیٹن حکومت نے شہری سیلاب سے بچاؤ کے لیے ایک جامع انفراسٹرکچر بلیو پرنٹ جاری کیا، جو اُس دہائی کے مسلسل طوفانوں اور بڑھتی شہری آبادی کے دباؤ کے جواب میں تیار کیا گیا تھا۔ 1970 کی دہائی میں ٹوکیو کو بارہا سیلابی صورتحال کا سامنا کرنا پڑا کیونکہ نکاسی کے پرانے نظام بوجھ برداشت نہیں کر پاتے تھے اور تیزی سے ہوتی کنکریٹ شدہ تعمیرات نے بارش کے قدرتی جذب کے راستے ختم کر دیے تھے۔ اس بلیو پرنٹ نے زیرزمین پانی ذخیرہ گاہوں، چوڑے دریا کناروں، کثیر سطحی ڈرینیج ٹنلز اور گرین واٹر پارکس پر مشتمل ایک مربوط نظام تجویز کیا، جسے زیادہ خطرے والے وارڈز میں تقسیم کیا جانا تھا۔ اس منصوبے میں طویل مدتی لینڈ یوز پلاننگ شامل تھی اور نئے رہائشی و صنعتی منصوبوں کے لیے لازمی قرار دیا گیا کہ وہ قابل نفوذ فرش، بارش کے پانی جمع کرنے والے ڈھانچے، اور اوور فلو کم کرنے کے نظام اپنائیں۔
یہ پالیسی جاپان میں سائنسی بنیادوں پر خطرات کی پیش گوئی کی طرف ابتدائی قدم بھی ثابت ہوئی۔ انجینئرز نے بارش کی کمپیوٹر سمولیشن اور زمینی ساخت کے ماڈلز استعمال کرتے ہوئے خطرناک علاقوں کی نشاندہی کی، جس کے نتیجے میں پہلی بار ٹوکیو کی زوننگ پالیسی میں سیلاب سے تحفظ شامل ہوا۔ سماجی طور پر، اس منصوبے نے شہری آبادی میں آگاہی بڑھائی اور محلہ کمیٹیوں نے گھروں میں سیلاب سے بچاؤ کی تیاریوں پر تربیتی پروگرام شروع کیے۔
وقت کے ساتھ یہ بلیو پرنٹ جاپان کے بڑے سیلابی انفراسٹرکچر منصوبوں کی بنیاد بنا، جن میں 1990 کی دہائی کے جدید اسٹورم واٹر ٹنلز شامل ہیں۔ ٹوکیو کا دنیا کے محفوظ ترین شہروں میں شمار ہونا اسی بلیو پرنٹ کا تسلسل ہے۔
On November 21, 1987, the Punjab Planning and Development Department introduced the Inter-District Agricultural Storage & Cold-Chain Enhancement Initiative, a landmark program designed to reduce post-harvest losses and stabilize farm incomes across central and southern Punjab. During the late 1980s, regions such as Okara, Sahiwal, Rahim Yar Khan, and Bahawalpur were experiencing increased production of perishable crops including vegetables, citrus, and fodder, yet the lack of structured storage facilities often resulted in wastage and major price fluctuations. The new initiative proposed the construction of standardized cold-storage units along canal-fed agricultural belts, ensuring that farmers could safely store produce instead of selling it at low off-season prices. The program also emphasized mobile cooling vans, district-level storage cooperatives, and the development of power-stable ‘agri-zones’, aimed at mitigating voltage instability that frequently damaged cooling equipment.
The policy was rooted in extensive field surveys and consultations with local growers, transporters, and market committees. It introduced early models of public–private partnerships, allowing private investors to operate storage facilities under government-regulated pricing mechanisms. By facilitating long-term preservation, the initiative significantly strengthened Pakistan’s internal vegetable and fruit supply chain. Farmers gained improved bargaining power, traders experienced lower transit spoilage, and urban markets began receiving more consistent supplies throughout the year.
Over the years, this initiative became a foundational element of Punjab’s agricultural modernization. It shaped later cold-chain policies of the 1990s and improved coordination between rural production zones and major urban consumption centres. Its long-term legacy lies in establishing the concept of district-level storage hubs, which eventually became central to Pakistan’s early agri-logistics reforms.
▪ Reference(s):
21 نومبر 1987 کو پنجاب پلاننگ اینڈ ڈیولپمنٹ ڈیپارٹمنٹ نے بین الاضلاعی زرعی اسٹوریج اور کولڈ چین میں بہتری کے منصوبے کی منظوری دی، جو اس وقت زرعی پیداوار کے بڑھتے ہوئے حجم کے باوجود کمزور ذخیرہ اندوزی کی وجہ سے بھاری بعد از فصل نقصان کا سامنا کرنے والے علاقوں کے لیے نہایت اہم قرار پایا۔ 1980 کی دہائی کے آخر میں اوکاڑہ، ساہیوال، رحیم یار خان اور بہاولپور جیسے اضلاع میں سبزیوں، ترشاوہ پھلوں اور چارے کی پیداوار میں تیزی آئی تھی، مگر مناسب کولڈ اسٹوریج نہ ہونے کے باعث یا تو اجناس ضائع ہوجاتیں یا پھر کسانوں کو ضرورت سے کم قیمتوں پر فروخت کرنا پڑتی تھی۔ اس نئے منصوبے نے نہری علاقوں کے ساتھ معیاری کولڈ اسٹوریج یونٹ قائم کرنے، موبائل کولنگ وینز متعارف کرانے، اور ڈسٹرکٹ سطح پر اسٹوریج کوآپریٹیوز بنانے کا خاکہ پیش کیا، تاکہ کسان فصلوں کو محفوظ رکھ سکیں اور سیزن سے باہر بہتر نرخ حاصل کرسکیں۔
یہ پالیسی مقامی کاشتکاروں، ٹرانسپورٹرز اور مارکیٹ کمیٹیوں سے کیے گئے تحقیقی سرویز کی بنیاد پر تشکیل دی گئی تھی۔ اس میں عوام اور نجی شعبے کے مشترکہ تعاون کا ماڈل بھی شامل تھا، جس میں نجی سرمایہ کار حکومتی نگرانی میں اسٹوریج مراکز چلاتے تھے۔ اس اقدام نے پاکستان کے اندرونی زرعی سپلائی چین کو مضبوط بنایا، ٹرانسپورٹ میں ضیاع کم ہوا، کاشتکاروں کی سودے بازی کی طاقت بڑھی، اور شہری مراکز میں اجناس کی سال بھر بہتر رسد ممکن ہوئی۔
وقت گزرنے کے ساتھ ساتھ یہ منصوبہ پنجاب کی زرعی جدیدکاری کا بنیادی ستون ثابت ہوا اور 1990 کی دہائی کی کولڈ چین پالیسیوں اور ایگرو لاجسٹک اصلاحات کے لیے بنیاد فراہم کی۔

On 11 December 2018, the Supreme Court of Pakistan, under the leadership of then Chief Justice Mian Saqib Nisar, imposed a strict and highly unusual restriction on the transfer, lease, and allotment of land in Sindh. The court directed that until the provincial land revenue record was fully computerised, no allotment, lease, or transfer of governme...
Read More →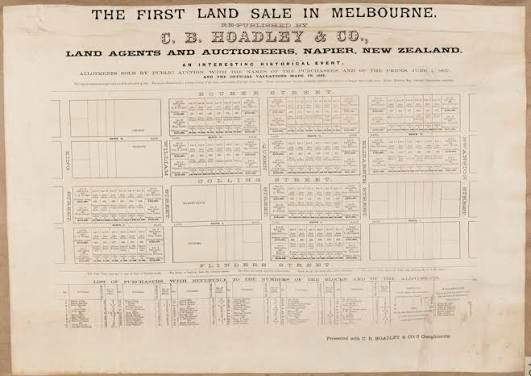
On October 10, 1885, Melbourne witnessed one of the most significant property events in its urban history when the city hosted its first large scale public land auction in the growing suburbs south of the Yarra River. At that time, Melbourne was experiencing a remarkable economic and population boom driven by gold rush prosperity, migration, and in...
Read More →
Across Pakistan, 31 December is designated as the annual Close of the revenue system, under which all land and property related records maintained by the Board of Revenue are formally closed on a yearly basis. This process encompasses all administrative levels, from the traditional patwari system to modern computerised land record offices. On 31...
Read More →
On November 12, 1885, Paris initiated a large-scale suburban expansion project inspired by Baron Haussmann’s earlier urban reforms. The French government sought to manage rapid industrial growth and population pressure by extending planned boulevards and housing layouts beyond the city walls. The expansion included public transport integration, w...
Read More →
On November 1, 2016, Pakistan inaugurated the Gwadar Free Zone under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), marking a milestone in regional industrial growth. The project aimed to transform Gwadar into a global logistics and manufacturing hub connecting South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. The zone offered tax holidays, investor incentive...
Read More →
The acquisition of land for the Model Town Society was one of the most remarkable and spirited chapters in its early history. Dewan Khem Chand and his...

Between 1921 and 1924, the land for Model Town Lahore was acquired in successive phases. The process began in 1921, shortly after the establishment of...
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!