
Syed Shayan Real Estate Archive

From Real Estate History
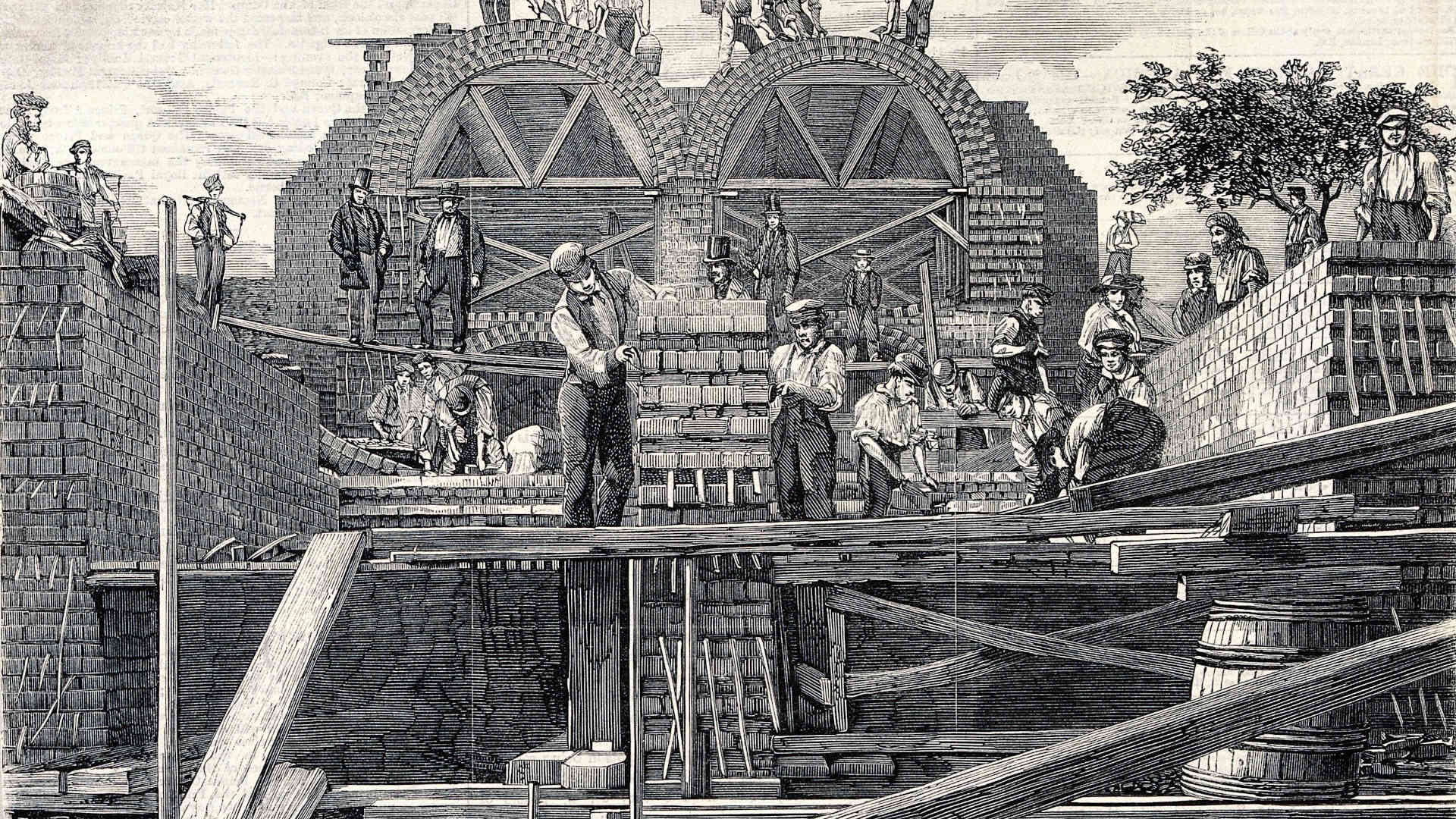
On November 11, 1894, the British Parliament approved the London Housing Reform Act to address worsening living standards in industrial London. The nineteenth century had transformed the city into a dense, polluted metropolis where entire families were crowded into small, unsanitary tenements. Poor ventilation, unsafe structures, and limited access to clean water caused repeated outbreaks of cholera and typhoid. The new law gave municipal authorities the power to clear slums, regulate building quality, and develop affordable public housing for workers. For the first time, government policy acknowledged housing as a public responsibility rather than a private market concern. The act introduced design standards for natural light, ventilation, and spacing between buildings, promoting the idea that healthy environments were essential for productivity and morality. Green spaces, public baths, and communal facilities became part of the urban design vocabulary. The legislation later inspired similar reforms across Europe and influenced colonial housing standards in South Asia and Africa. The London Housing Reform Act is now seen as a foundational step toward state-led social housing and modern urban planning that values public welfare, hygiene, and human dignity.
▪ Reference(s):

11 نومبر 1894 کو برطانوی پارلیمنٹ نے لندن ہاؤسنگ ریفارم ایکٹ منظور کیا تاکہ صنعتی دور کے لندن میں بگڑتے رہائشی حالات کو بہتر بنایا جا سکے۔ انیسویں صدی میں تیز رفتار صنعتی ترقی نے لندن کو ایک گنجان، آلودہ شہر میں بدل دیا تھا جہاں پورے خاندان تنگ، غیر صحت مند اور غیر محفوظ عمارتوں میں رہنے پر مجبور تھے۔ ناقص ہوا داری، آلودہ پانی اور خطرناک تعمیرات نے ہیضہ اور ٹائیفائیڈ جیسی وباؤں کو عام بنا دیا تھا۔ اس قانون کے تحت مقامی حکام کو اختیار دیا گیا کہ وہ کچی آبادیوں کو مسمار کر سکیں، تعمیرات کے معیار کو بہتر بنائیں اور مزدور طبقے کے لیے سستی عوامی رہائش فراہم کریں۔ پہلی بار ریاست نے رہائش کو عوامی ذمہ داری کے طور پر تسلیم کیا۔ ایکٹ میں قدرتی روشنی، ہوا داری اور عمارتوں کے درمیانی فاصلے کے لیے معیارات مقرر کیے گئے تاکہ صحت مند ماحول کو فروغ دیا جا سکے۔ اس دور میں پارکوں، عوامی غسل خانوں اور کمیونٹی سہولتوں کو شہری ڈیزائن کا لازمی حصہ بنایا گیا۔ بعد ازاں یہ قانون یورپ بھر میں شہری اصلاحات کے لیے ایک نمونہ بنا اور نوآبادیاتی علاقوں میں بھی تعمیراتی اصولوں کو متاثر کیا۔ لندن ہاؤسنگ ریفارم ایکٹ کو آج ریاستی سرپرستی میں سماجی رہائش اور جدید شہری منصوبہ بندی کی بنیاد سمجھا جاتا ہے جو عوامی فلاح اور انسانی وقار کو مرکزی اہمیت دیتا ہے۔
On November 11, 1952, the Government of Pakistan approved the Karachi Land Reclamation and Port Housing Development Plan to support the growing workforce of Karachi Port and nearby industries. Following independence, Karachi had transformed into a vibrant trade hub with massive migration from across South Asia. However, housing shortages and unsafe settlements had become a serious urban challenge. The plan aimed to reclaim swampy coastal areas near the harbor and convert them into structured residential, commercial, and industrial zones. Engineers from the Karachi Improvement Trust, assisted by British and local planners, designed modern layouts with wide roads, drainage systems, and low-cost housing quarters for dockworkers and small traders. It introduced Pakistan’s first formal zoning framework, separating residential and industrial areas to improve urban efficiency and livability. The project also emphasized providing schools, clinics, and markets within each neighborhood to promote balanced community development. Over the years, the reclaimed areas evolved into key districts that shaped the city’s growth pattern. This initiative is remembered as one of the earliest examples of planned urban expansion in Pakistan, combining engineering innovation with social welfare objectives.
▪ Reference(s):
11 نومبر 1952 کو حکومتِ پاکستان نے کراچی لینڈ ری کلیمیشن اور پورٹ ہاؤسنگ ڈویلپمنٹ پلان کی منظوری دی تاکہ کراچی کی بندرگاہ اور صنعتی علاقوں میں کام کرنے والے مزدوروں کی بڑھتی ہوئی رہائشی ضروریات پوری کی جا سکیں۔ آزادی کے بعد کراچی ایک مصروف تجارتی مرکز میں بدل چکا تھا اور برصغیر کے مختلف علاقوں سے ہجرت نے شہر کی آبادی میں بے پناہ اضافہ کیا۔ تاہم رہائش کی کمی اور غیر محفوظ بستیاں ایک سنگین مسئلہ بن گئی تھیں۔ اس منصوبے کا مقصد ساحلی دلدلی زمینوں کو خشک کر کے انہیں منظم رہائشی، تجارتی اور صنعتی علاقوں میں تبدیل کرنا تھا۔ کراچی امپروومنٹ ٹرسٹ کے انجینئرز نے مقامی اور برطانوی ماہرین کے تعاون سے جدید منصوبہ بندی کے تحت کشادہ سڑکیں، نکاسیٔ آب کا نظام اور مزدوروں کے لیے کم قیمت مکانات تیار کیے۔ پہلی بار پاکستان میں باقاعدہ زوننگ فریم ورک متعارف ہوا جس کے تحت رہائشی اور صنعتی علاقوں کو الگ کر کے شہری کارکردگی بہتر بنائی گئی۔ منصوبے میں اسکول، کلینک اور مارکیٹیں بھی شامل کی گئیں تاکہ متوازن کمیونٹی ترقی ممکن ہو۔ وقت کے ساتھ یہ علاقے کراچی کی ترقی کے اہم حصے بن گئے۔ یہ منصوبہ پاکستان میں منصوبہ بند شہری توسیع کی ابتدائی اور نمایاں مثال سمجھا جاتا ہے جس نے انجینئرنگ جدت اور سماجی فلاح کو ایک ساتھ جوڑا۔
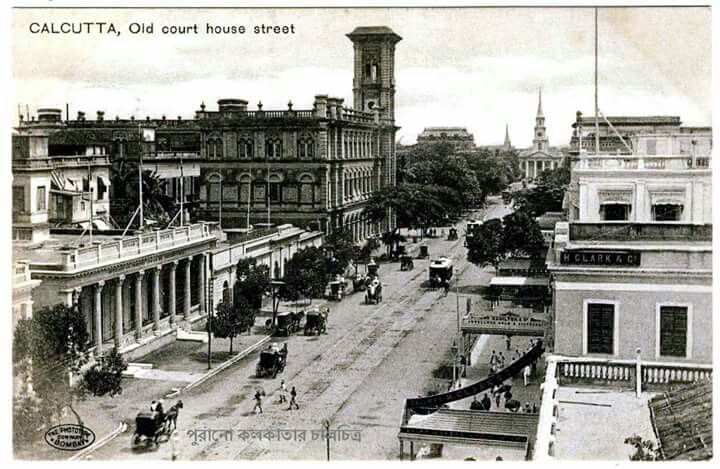

On October 10, 1924, the Registrar of Co-operative Societies in the Bengal Presidency recorded one of the earliest applications for a Residential Cooperative Housing Society in Calcutta, now Kolkata. This marked a turning point in South Asia’s urban development when the cooperative principle, previously used for credit and agriculture, was extend...
Read More →On October 26, 2005, the US housing bubble reached its zenith, marking the peak of unsustainable price growth that would soon trigger the global financial crisis. Property values had soared to unprecedented levels driven by speculative investments, subprime lending practices, and financial innovations that masked underlying risks. The market showed...
Read More →On 26 November 1947 the Government of West Punjab completed its first major survey of Evacuee Property, documenting thousands of abandoned agricultural lands urban buildings and industrial units left behind during the mass migration of Partition. The survey established the first verified list of transferable assets that could be allocated to incomi...
Read More →
On 2 February 1665, British forces formally consolidated their control over the Dutch colonial settlement of New Amsterdam, located in what is now the Manhattan area of New York City. On this occasion, the settlement was renamed New York. The earliest known name of the area was Manahatta or Mannahatta, a term used by the indigenous Lenape people, ...
Read More →
On November 22, 1983, the French Ministry of Transport unveiled a nationwide rail safety modernization blueprint to respond to rising commuter volumes and expanding suburban zones around major cities including Paris, Lyon, and Marseille. The early 1980s had seen frequent near-accident incidents due to outdated signalling systems, manual switching i...
Read More →
The acquisition of land for the Model Town Society was one of the most remarkable and spirited chapters in its early history. Dewan Khem Chand and his...

Between 1921 and 1924, the land for Model Town Lahore was acquired in successive phases. The process began in 1921, shortly after the establishment of...
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!