
Syed Shayan Real Estate Archive

From Real Estate History

On November 25, 1982, the Government of Punjab finalized its first pre master planning guidelines to manage accelerating urban growth in Lahore, Rawalpindi, Faisalabad, Multan, and Gujranwala. During the late 1970s and early 1980s, these cities witnessed rapid expansion marked by informal subdivisions, inadequate street layouts, and insufficient drainage systems. To address these challenges, the new guidelines introduced early land assessments, structured plotting rules, and basic zoning coordination that would help authorities identify development pressures before colonies expanded uncontrollably. The policy particularly focused on fringe zones, where agricultural land was quickly being converted into speculative residential pockets without formal planning oversight.
The guidelines required pre development surveys to document soil stability, natural drainage channels, and existing right-of-way pathways, allowing planners to create more sustainable layouts. They also made cadastral verification mandatory to minimize overlapping land claims, which had become a rising issue in fast-growing districts. Alongside technical steps, the government launched training initiatives for patwaris, junior planners, and municipal engineers to improve mapping accuracy and strengthen basic documentation practices.
The policy recommended a phased model for integrating private housing schemes into municipal systems through shared contributions toward link roads, water supply lines, and sewer networks. This helped reduce the long-term burden on municipal budgets. The 1982 framework later shaped Punjab’s structured planning reforms in the 1990s by standardizing NOC checks and promoting more data-driven approvals. Although preliminary, these guidelines became a foundation for modern peri-urban zoning practices and remain influential in shaping organized growth in expanding cities.
▪ Reference(s):

25 نومبر 1982 کو حکومت پنجاب نے پری ماسٹر پلاننگ گائیڈلائنز کو حتمی شکل دی جن کا مقصد لاہور، راولپنڈی، فیصل آباد، ملتان اور گوجرانوالہ میں تیزی سے بڑھتی ہوئی شہری توسیع کو مؤثر طریقے سے منظم کرنا تھا۔ 1970 کی دہائی کے آخر اور 1980 کے آغاز میں غیر منصوبہ بند رہائشی بستیاں، بے قاعدہ گلیوں کا نظام اور نکاسی آب کی کمی بڑے انتظامی مسائل بن چکے تھے۔ ان مسائل کو دیکھتے ہوئے نئی گائیڈلائنز میں ابتدائی زمینی سروے، منظم پلاٹنگ اصول اور بنیادی زوننگ کوآرڈینیشن شامل کی گئی تاکہ کالونیاں بے قابو انداز میں نہ پھیلیں۔ پالیسی خصوصاً مضافاتی علاقوں پر مرکوز تھی جہاں زرعی زمین تیزی سے رہائشی مقاصد کے لیے تبدیل ہو رہی تھی اور مناسب جانچ کے بغیر تعمیرات بڑھ رہی تھیں۔
گائیڈلائنز کے مطابق پری ڈویلپمنٹ سروے میں مٹی کا جائزہ، قدرتی نالوں کی نشاندہی اور موجودہ راستوں کا ریکارڈ شامل کرنا لازمی قرار دیا گیا تاکہ مستقبل کے لیے پائیدار سڑک اور نکاسی آب کا نظام بنایا جا سکے۔ اس کے ساتھ کیڈسٹرل ریکارڈ کی درست تصدیق کو بھی لازمی بنایا گیا تاکہ پلاٹوں کی حدود کے تنازعات کم ہوں۔ حکومت نے اس سلسلے میں پٹواریوں اور پلانرز کی تربیت کے پروگرام بھی شروع کیے تاکہ نقشہ سازی اور ریکارڈ مرتب کرنے کے طریقہ کار میں بہتری آئے۔
پالیسی میں نجی ہاؤسنگ سکیموں کو میونسپل نظام میں مرحلہ وار شامل کرنے کے لیے مشترکہ مالی معاونت کا ماڈل پیش کیا گیا، جس سے مستقبل میں سڑکوں اور نکاسی آب پر بجٹ کا دباؤ کم ہوا۔ 1982 کا یہ فریم ورک بعد میں 1990 کی دہائی کی منصوبہ بندی اصلاحات کی بنیاد بنا اور آج بھی تیزی سے بڑھتے ہوئے شہروں میں منظم شہری ترقی کی رہنمائی کرتا ہے۔
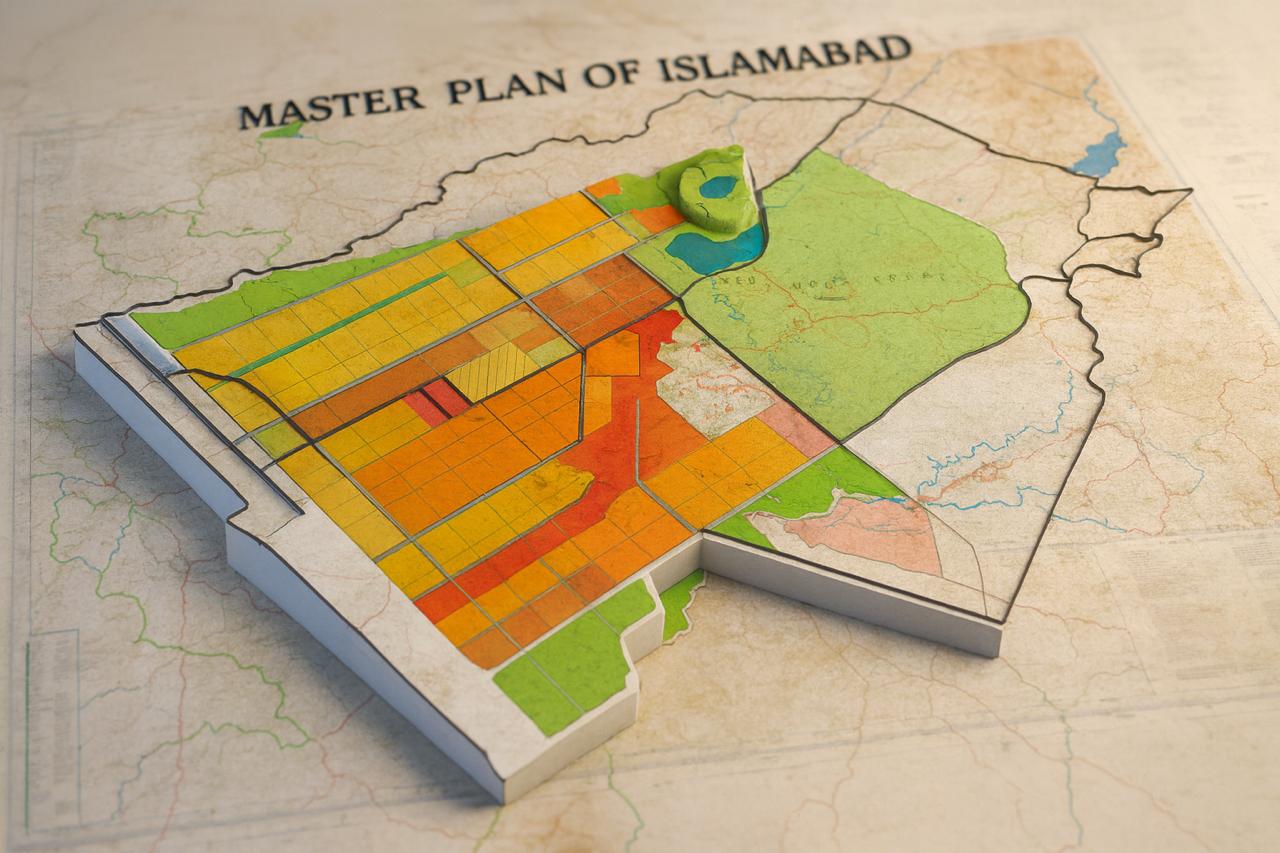
On 4 December 2002, the federal government approved the first comprehensive technical review of Islamabad’s 1960 master plan. The cabinet was informed that rapid population growth, uncontrolled commercialisation and extensive public and private construction had fundamentally altered the original plan, while land-use patterns and designated green...
Read More →
On November 1, 2016, Pakistan inaugurated the Gwadar Free Zone under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), marking a milestone in regional industrial growth. The project aimed to transform Gwadar into a global logistics and manufacturing hub connecting South Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. The zone offered tax holidays, investor incentive...
Read More →
On October 22, 1963, groundbreaking condominium legislation was enacted, creating the legal framework for individual ownership of units within multi-story residential buildings. This revolutionary law established the concept of 'air rights' ownership and created mechanisms for shared ownership of common areas, maintenance responsibilities, and gove...
Read More →On October 31, 2003, the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, officially claimed the title of the world's tallest residential building, marking a major milestone in architectural and urban innovation. Standing 452 meters tall, the twin towers symbolized Malaysia’s rapid modernization and its emergence as a global real estate powerhouse. Des...
Read More →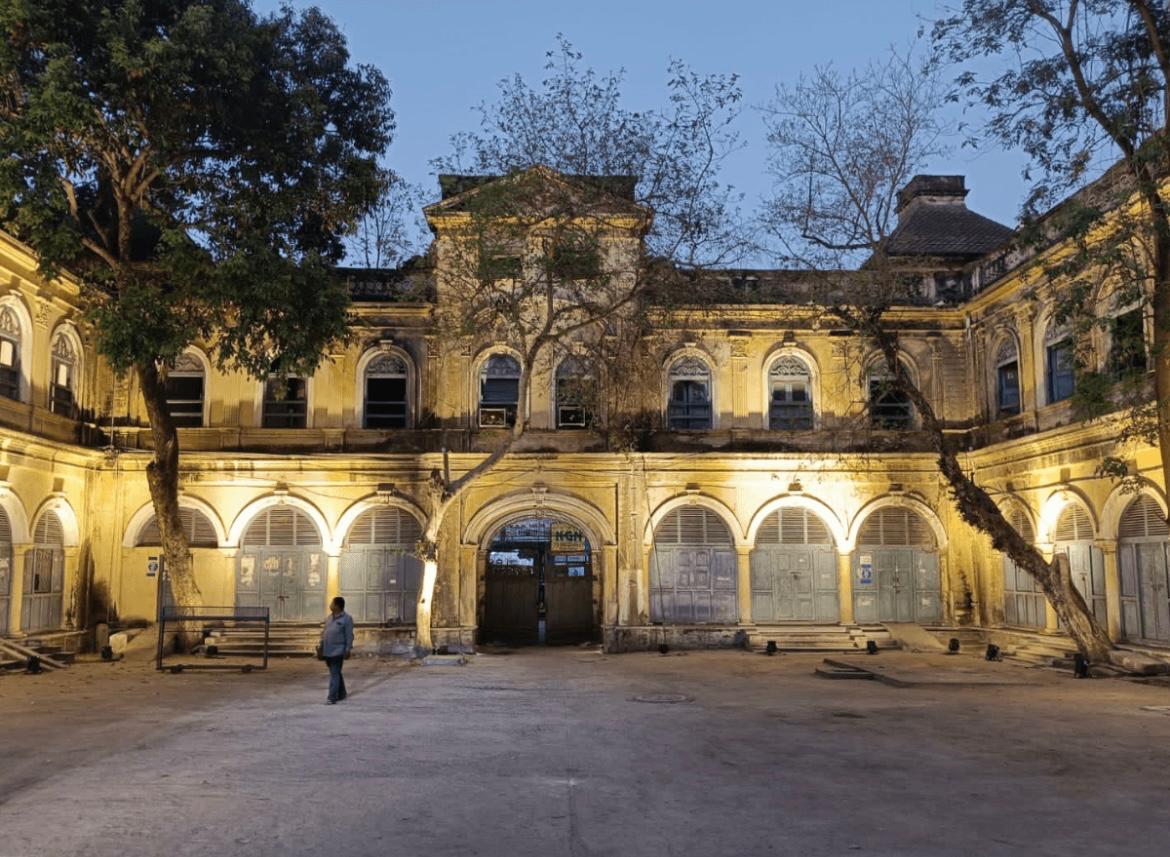
On 24 January 1965, the historic Sardar Mahal, located in Hyderabad, was placed under official municipal control following the failure to clear outstanding property tax dues. After the takeover, the premises were repurposed for municipal administrative use. The action was carried out by the Hyderabad Municipal Corporation, which was later reorgani...
Read More →
The acquisition of land for the Model Town Society was one of the most remarkable and spirited chapters in its early history. Dewan Khem Chand and his...
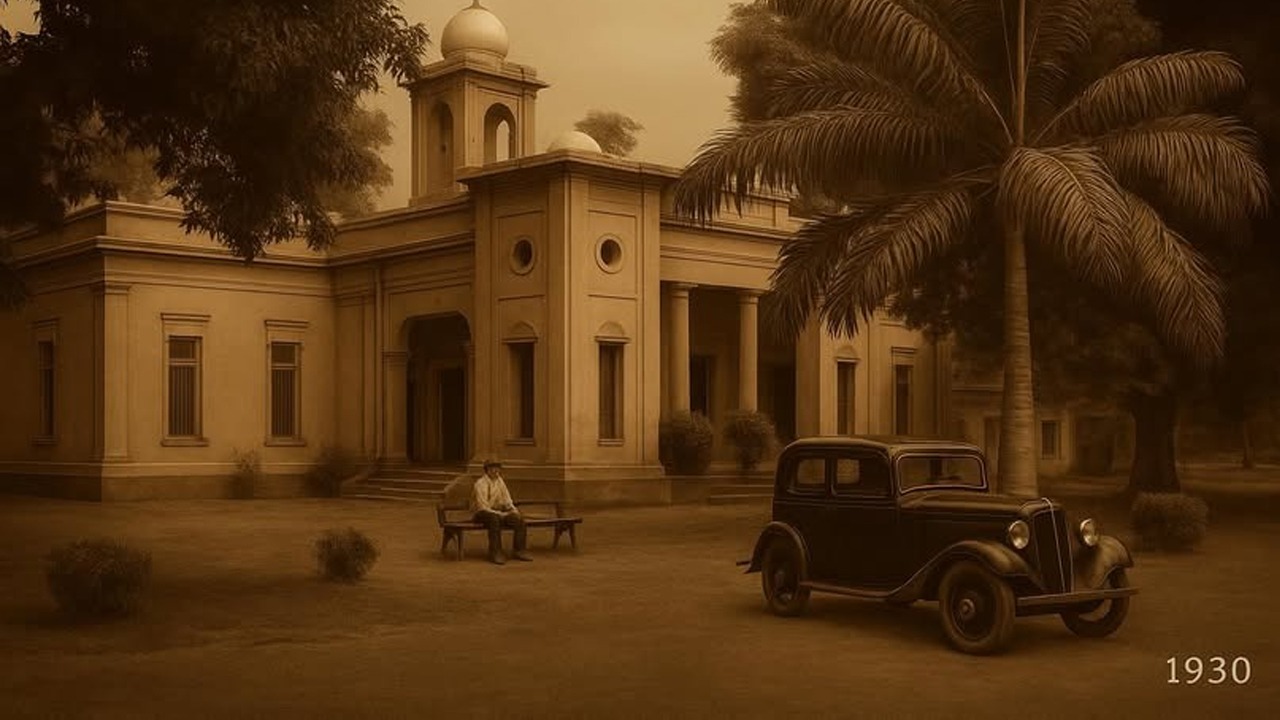

Between 1921 and 1924, the land for Model Town Lahore was acquired in successive phases. The process began in 1921, shortly after the establishment of...
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!